
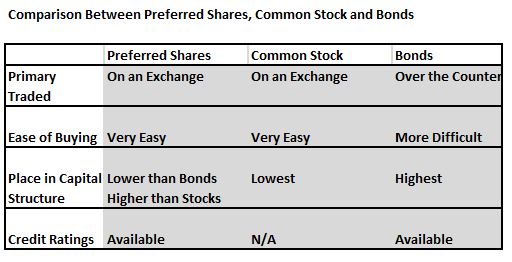
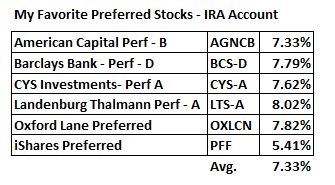
Most people who follow my blog know that I like Preferred Shares in my High Yield IRA account. High on my list are bank preferred shares, which tend to be a very reliable source of income.
Here is a really special situation that you might want to take advantage of.
The Preferred Stock is BAC-L, Bank of America, 7.25% Non-Cumulative Convertible Preferred Stock, Series L. This is a $1,000 par value preferred, that pays $72.50 a year in “qualified dividends”. The key to this stock is the “Convertible” designation, these shares won’t be called because the conversion price is probably not achievable. It is convertible into 20 shares of BAC if the common trades above $65 (130% of $50) for 20 out of 30 consecutive days. However the current BAC common price is about $16.
Normally I would never buy a preferred stock well above its par value ($1,000), it is currently trading at $1,213. However, this is a 6% yield even at a premium. In addition, if you look at a multi-year chart, there is a lot of price support at current levels.
Bank of America sold this preferred back during the financial crisis and is now stuck with it. They can’t call it! They could repurchase the shares in the open market, but this would further drive up the price.
This is a great deal!
I bought another chunk today using a limit order at $1,213.













 I consult with dozens of CEO’s from start-up’s to 20 years old small businesses, many of them have the same problems.
I consult with dozens of CEO’s from start-up’s to 20 years old small businesses, many of them have the same problems.



